1-The threshold for the detection of ordors is ____________ and adaption to odors occurs___________
a).high, quickly b).high, slowly
c).low, quickly d).low, slowly
2-The axons of the olfactory neurons pass through the foramina of the _____________ to synapse with
mital or tufted cells in the __________________.
a).cribiform plate, olfactory tract b).cribiform plate, olfactory bulb
c).nasal bone, olfactory tract d).nasal bone, olfactory bulb b).
3-Which cells proliferate to replace lost olfactory cells?
a).basal cells b).mitral cells
c).olfactory hairs d).tufted cells a).
4-Which of the following is NOT true of olfactory neurons?
a).The axons of the olfactory neurons combine to form the olfactory nerves
b).The olfactory neurons synapse with cells in the olfactory bulb.
c).Olfactory neurons have receptors that react with ordorants dissolved in fluid.
d).Olfactory neurons are uni-polar neurons. d).
5-Which region of the olfactory cortex is involved in conscious perception of smell?
a).intermediate olfactory area b).lateral olfactory area
c).medial olfactory area d).superior olfactory area b).
6-Which region of the olfactory cortex is connected to the limbic system?
a).intermediate olfactory area b).lateral olfactory area
c).medial olfactory area d).superior olfactory area c).
7-Which region of the olfactory cortex aids in modifying sensory information in the olfactory bulb?
a).intermediate olfactory area b).lateral olfactory area
c).medial olfactory area d).superior olfactory area c).
8-Where within the nasal cavity is the olfactory epithelium located?
a).Anterior and lateral portion of the nasal cavity.
b).Posterior and lateral portion of the nasal cavity.
c).Interior portion of the nasal cavity.
d).Superior portion of the nasal cavity. d).
9-Which type of papillae have no taste buds associated with them?
a).circumvallate b).filiform
c).foliate d).fungiform b).
10-Which type of papillae have the most sensitive taste buds associated with them?
a).circumvallate b).filiform
c).foliate d).fungiform c).
11-How many primary tastes have been identified?
a).4 b).5
c).7 d).400 b).
12-Which of the following cranial nerves does not transmit taste sensation?
a).Trigeminal (V) nerve b).Facial (VII) nerve
c).Glossopharyngeal (IX) nerve d).Vagus (X) nerve a).
13-Identify the location of the taste area of the cortex.
a).precentral gyrus b)-postcentral gyrus
c).thalamus d).temporal lobe b).
14-Which of the following primary tastes do not cause depolarization of the gustatory through a G protein
mechansim?
a).bitter b).sweet
c).salty d).umami c).
15-Which of the following primary tastes do not require a substance to bind to a receptor on the gustatory
hairs of taste cells?
a).salty b).bitter
c).sweet d).umami a).
16-Which of the following describe the relationship between olfaction and gustation?
a).Gustatory hairs can also detect odorants.
b).Olfactory sensations provide information about a substance that may be thought of as taste.
c).Olfactory hairs can also detect tastants.
d).There is no relationship between the olfactory and gustatory sense. c).
17-Which taste sensation is the most sensitive?
a).bitter b).salty
c).sweet d).umami a).
18-Which muscle closes the eyelid when it contracts?
a).inferior rectus b).levator palpebrae suprioris
c).orbicularis oculi d).superior oblique c).
19-Which muscle raises the upper eyelid when it contracts?
a).levator palpebrae superioris b).orbicularis oculi
c).superior oblique d).superior rectus a).
20-Which of these extrinsic eye muscles is NOT controlled by the oculomotor nerve?
a).inferior oblique b).inferior rectus
c).medial rectus d).superior oblique d).
21-Which of these extrinsic eye muscles is controlled by the trochlear nerve?
a).inferior rectus b).medial rectus
c).superior oblique d).superior rectus c).
22-Identify the three layers of the eye in from the outer most layer to the inner most layer.
a).fibrous tunic, nervous tunic, vascular tunic
b).fibrous tunic, vascular tunic, nervous tunic
c).nervous tunic, fibrous tunic, vascular tunic
d).vascular tunic, fibrous tunic, nervous tunic b).
23-What eye layer is referred to in the quote "Don't fire until you see the whites of their eyes"?
a).conjunctiva b).choroid
c).retina d).schera d).
24-The transparent anterior portion of the outer eye coat which allows light rays to enter the interior of the
eye is the ______________________________
a).conjunctiva b).cornea
c).iris d).sclera b).
25-The colored (blue, brown, green) portion of the eye, as seen in an anterior view, is which of the
following?
a).choroid b).ciliary body
c).cornea d).iris d).
26-The watery fluid we call "tears" is secreted by ___________________________
a).ceruminous glands b).eccrine glands
c).lacrimal glands d).tarsal glands c).
27-Aqueous humor is secreted by the _______________ ; it flows out of the posterior chamber through the
pupil into the anterior chamber wherer it is reabsorbed at a ring-like blood vessel called the _________
a).ciliary process; canal of Schlem b).ciliary process; eustachian tube
c).iris; canal of Schlem d).iris; eustachian tube a).
28-When intraocular pressure increases because aqueous humor is not reabsorbed as fast as it is produced,
______________ occurs, which can lead to blindness.
a).astigmatism b).cataract
c).emmetropia d).glaucoma d).
29-All of the following are part of the middle "vascular" tunic of th eye EXCEPT
a).choroid b).ciliary body
c).iris d).cornea d).
30-A sty is an inflammation of what type of gland associated with follicles of the eyelashes?
a).ciliary gland b).meibomian gland
c).sebacerous gland d).tarsal gland a).
31-After washing across the eyes, "tears" enter the nasal cavity through which of the following?
a).canals of Schlemm b).collecting ducts
c).eustachian tubes d).nasolacrimal ducts d).
32-Which of the following is NOT a function of the sclera?
a).It provides attachment points for muscles that move the eye.
b).It helps nourish the retina.
c).It helps maintain the shape of the eye.
d).it protects internal structures of the eye. b).
33-All of the following are intrinsic eye muscles EXCEPT the _________________
a).ciliary muscles b).dilator pupillae
c).sphincter pupillae d).superior oblique d).
34-From superficial to deep, the three main cell layers of the sensory retina are
a).photoreceptors - bipolar cells - ganglion cells.
b).ganglion cells - bipolar cells - photoreceptors.
c).bipolar cells - ganglion cells - photoreceptors.
d).photoreceptors - ganglion cells - bipolar cells a).
35-Clouding of the lens occurs in which of these eye disorders?
a).cataract b).glaucoma
c).strabismus d).trachoma a).
36-Which of the following is NOT true about the cornea?
a).It is the main place at which refraction of light occurs.
b).It is transparent.
c).It is nourished by the vitreous humor.
d).It is avascular. c).
37-Which of the following is NOT a feature of the retina?
a).ganglion cells b).photoreceptors
c).optic chiasma d).optic disc c).
38-Which of the following statements about the lens is NOT true?
a).It is biconvex.
b).It is attached to the retina by suspensory ligaments.
c).It helps to focus light on the retina.
d).It is covered by a highly elastic, transparent capsule. b).
39-At which of the following locations do blood vessels and nerves enter or exit the eye?
a).fovea centralis b).optic chiasma
c).optic disc d).ora serrata c).
40-All of the following are correctly paired EXCEPT_____________________
a).canal of Schlemm - aqueous humor
b).ciliary body - iris
c).retina - suspensory ligaments
d).vitreous humor - posterior compartment c).
41-Contraction of which of the following muscles is involved with changing the shape (thickening) of the lens?
a).ciliary muscles b).circular muscles of the iris
c).orbicularis oculi d).radial muscles of the iris a).
42-If the ciliary muscles contract, the suspensory ligaments _________and the lens ____________.
a).pull; flattens b).relax; flattens
c).pull; thickens d).relax; thickens d).
43-What happens when the ciliary muscles relax?
a).The suspensory ligaments pull and the lens flattens.
b).The suspensory ligaments relax and the lens flattens.
c).The suspensory ligaments pull and the lens thickens.
d).The suspensory ligaments relax and the lens thickens. a).
44-Which layer of the eye contains the photoreceptor cells?
a).choroid b).ciliary body
c).retina d).sclera c).
45-Which of the following is commonly called the "blind spot" of the eye because it lacks photoreceptor cells?
a).canal of Schlemm b).fovea centralis
c).optic disc d).pupil c).
46-An eye that is too long, or "oval," results in poor distance vision, a disorder called nearsightedness or
a).astigmatism. b).hyperopia.
c).myopia. d).presbyopia. c).
47-When light strikes the visual pigment rhodopsin is activated which then activates __________
thus resulting in the ____________ of the rod cells.
a).opsin, depolarization b).opsin, heperpolarization
c).transducin, depolarization d).transducin, hyperpolarization a).
48-Which of the following is NOT true about cones compared to rods?
a).Cones produce color images rods do not.
b).Cones contain the supstance rhodopsin.
c).Cones are less sensitive to light.
d).Cones produces sharp, clear images. b).
49-Which of the following is NOT true about rods compared to cones?
a).Rods produce black and white but not color images.
b).Rods are most numerous in the fovea.
c).Rods contain rhodopsin.
d).Rods produce general outlines of objects rather than sharp images b).
50-Which of the following statements aobut nerve fibers of the optic nerves is true?
a).The nasal fibers from both retinas crossover at the optic chiasm.
b).the temporal fibers from both retinas crossover at the optic chiasm.
c).The nasal fibers from the left and the temporal fibers from the right retina crossover
at the optic chiasm.
d).The nasal firbers from the right and the temporal fibers from the left retina crossover
at the optic chiasm. a).
51-Which of the following is the location in the retina at which the sharpest images are produced?
a).fovea centralis b).optic chiasm
c).optic disc d).ora serrata a).
52-Image formation depends on refraction, the bending of light. At which location does the greatest
amount of refraction occur?
a).aqueous humor b).cornea
c).lens d).vitreous humor b).
53-Which of the following is the main factor affecting the depth of focus?
a).accommodation of the lens b).constriction of the pupil
c).convergence of the eyes d).refraction of light rays b).
54-The only retinal cells that produce action potentials are the ______________________
a).bipolar cells b).ganglion cells.
c).photoreceptor cells. d).pigmented epithelium. b).
55-In the dark the inward diffusion of ______________ causes rod cells to partially depolarize and
to release the neurotransmitter ____________ from their synaptic ends to inhibit or stimulate rod cells.
a).K+; acetylcholine b).K+ ; glutamate
c).Na+ ; acetylcholine d).Na+ , glutamate d).
56-When rhodopsin absorbs a photon of light, ____________ is converted to _____________and
dissociates from opsin which triggers ractions leading to the closure of ___________ channels in
the outer segments of rod cells.
a).cis-retinal ; trans-retinal ; K+ b).cis-retinal ; trans-retinal ; Na+
c).trans-retinal ; cis-retinal , K+ d).trans-retinal ; cis-retinal ; Na+ b).
57-Which of the following pairs of structures are involved in regulating the amount of light
that enters the eyes?
a).ciliary bodies adn suspensory ligaments
b).ciliary bodies and eyelids
c).ciliary bodies and irises
d).iris and eyelids d).
58-Photoreceptors in the human eye are capable of detecting and responding to wavelengths in
which of the following ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum?
a). 0 - 125 nm b). 400 - 700 nm
c). 20 - 20,000 nm d). 1,000 - 10,000 nm b).
59-All of the following are important in bringing an image to focus on the retina when viewing
an viewing an object close ot the eye EXCEP ______________________
a).accommodation of the lenses b).constriction of the pupils
c).flattening of the lenses d).convergence of the eyes c).
60-Axons of which of the following type of cells exit the eye in the optic nerve?
a).rods b).bipolar
c).ganglion d).cones c).
61-As you view your right index finger moving toward the tip of your nose, all of the following
occur EXCEPT __________________________
a).the lenses thicken b).ciliary muscles relax
c).the eyes rotate medially d).the diameter of the pupils decreases b).
62-Which of the following is a possible explanation for a person losing all vision in their left eye?
a).damage to the left occipital lobe
b).damage to the left lateral geniculate nucleus
c).damage to the left optic nerve
d).a lesion in the left optic tract c).
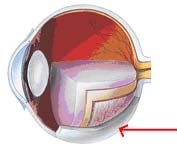
63-Identify the labeled structure in the diagram.
a).aqueous humor b).choroid coat
c).retina d).vitreous humor c).
64-Identify the labeled structure in the diagram.
a).optic chiasm b).optic nerve
c).optic tract d).retina c).
65-Identify the labeled structure in the diagram.
a).conjunctiva b).cornea
c).pupil d).lens b).
66-Identify the labeled structure in the diagram.
a).choroid coat b).cilary body
c).suspensory ligaments d).pupil b).
67-Identify the labeled structure in the diagram.
a).conjunctiva b).retina
c).sclera d).vitreous humor c).
68-which of the following is the passageway between the middle ear and the pharynx?
a).eustachian tube b).external auditory meatus
c).oval window d).semi-circular canals a).
69-Which auditory ossicle is attached to the tympanic membrane?
a).anvil b).incas
c).malleus d).stapes c).
70-Which auditory ossicle causes the oval window to move in and out, setting fluid in the inner ear
in motion?
a).incas b).malleus
c).stapes d).stapepedius c).
71-What fluid is located between the bony and membranous labyrinths within the inner ear?
a).aqueous humor b).endolymph
c).perilymph d).vitreous humor c).
72-The receptor cells for hearing are located on the upper surface of what membrane?
a).basilar membrane b).tectorial membrane
c).tympanic membrane d).vestibular membrane a).
73-Which of the following is loacted within the vestibule of the near?
a).crista ampullaris b).helicotrema
c).macula d).organ of Corti c).
74-Fluid in the scala vestbuli communicates with fluid in the scala tympai by way of the
a).canal of Schlemm b).eustachian tube
c).helicotrema d).round window c).
75-All of the following are part of the cochlea EXCEPT _________________________
a).cochlear duct b).scala tympani
c).scala vestibuli d).utricle d).
76-The name for one of the structures involved in detecting a change in the position of the head with respect
to gravity or static equibrium is ____________________________
a).ampulla. b).crista ampullaris.
c).helicotrema d).macula. d).
77-Each ampulla of a semicircular canal contains a (n) ______________, which is involved in sensing
movement of the head or dynamic equilibrium.
a).crista ampullaris b).helicotrema
c).macula d).organ of Corti a).
78-The receptor cells for hearing, hair cells, are located within the ______________________
a).macula b).organ of Corti
c).utricle d).vestibule b).
79-Otoliths are crystals of _________________ associated with the _________________.
a).calcium carbonate; crista ampullaris
b).calcium carbonate ; macula
c).calcium phosphate ; crista ampullaris
d).calcium phosphate; macula b).
80-Which of the following would NOT be part of the nerve pathway involved in conducting sensory impulses
to the auditory cortex?
a).medulla oblongata b).midbrain
c).spinal cord d).thalamus c).
81-The sensation of hearing occurs when sensory impulses from the ears are transmitted to the auditory
cortex in the ________________ lobe from the _________________nerve.
a).occipital ; trochlear b).occipital ; vestibulocochlear
c).temporal ; trochlear d).temporal ; vestibulocochlear d).
82-What is the name of the short tube that conveys sound waves to the tympanic membrane?
a).external auditory meatus b).auditory tube
c).canal of Schlemm d).eustachian tube a).
83-Movement of the _____________ membrane causes hair cell microvilli to bend back and forth.
a).basilar b).tectorial
c).tympanic d).vestibular a).
84-Damage to the vestibulocochlear nerve would result is some loss of __________________
a).hearing and balance b).hearing and taste
c).smell d).taste a).
85-Identify the correct order in which vibratons travel through the auditory ossicles.
a).incus, malleus, stapes b).stapes, malleus, incus
c).malleus, incus, stapes d).stapes, incus, malleus c).
86-Identify the primary function of the structure labeled in the diagram.
a).hearing b).movement of the head
c).position of the head d).vision a).
87-Identify the primary function of the structure labeled in the diagram.

a).hearing b).movement of the head
c).position of the head d).vision b).
88-Identify the primary function of the structure labeled in the diagram.
a).hearing b).movement of the head
c).position of the head d).vision c).
















































ไม่มีความคิดเห็น:
แสดงความคิดเห็น